
Cooling Crystallizers

Functioning of Cooling Crystallizers
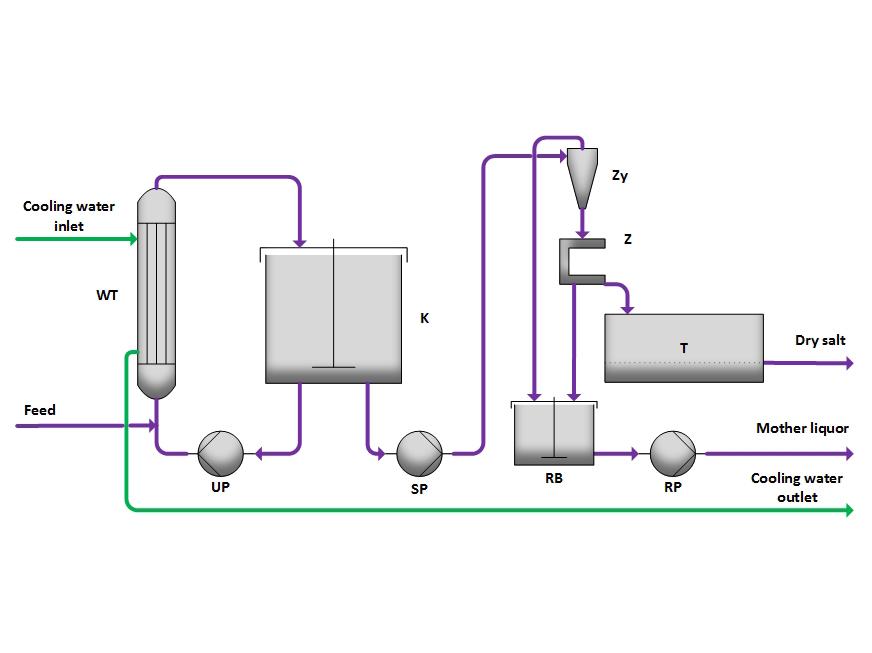
The nearly saturated solution is introduced into the crystallizer (K) or its circulation line. Here, it is mixed with the circulating solution and only slightly cooled in the cooler (WT) to minimize spontaneous nucleation and encrustation. In the crystallizer (K), supersaturation is reduced through crystal growth.
The resulting suspension is pumped by the suspension pump (SP) to the cyclone (Zy), where it is thickened. Subsequently, in the centrifuge (Z), the liquid is separated, and the salt is dried in the dryer (T).
Cooling Crystallizers Principle
Cooling crystallizers work based on the principle that reducing the temperature of a solution decreases the solubility of a contained salt, leading to the crystallization of the salt.
Advantages of Cooling Crystallizers
- High boiling point elevation: Suitable for solutions with a high boiling point elevation.
- Atmospheric pressure: Operation at atmospheric pressure possible.
- Flexible operation: Partial load operation for flexible process adaptation.
- Versatile applications: Suitable for various industrial applications.
Variants of Cooling Crystallizers
- Salt separation: Optional integration of a salt separation unit.
- Multiple circulation loops: Operation during cleaning for critical salts.
- Operating mode: Choice between continuous and batch operation.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why are cooling crystallizers relevant in various industries?
Cooling crystallizers enable efficient recovery and purification of salts, which is significant in various industries, such as the chemical industry.
What role does minimal cooling in the cooler play?
The slight cooling in the cooler minimizes spontaneous nucleation and encrustation, leading to more efficient crystallization and higher product quality.
What advantages do cooling crystallizers offer over other crystallization methods?
Cooling crystallizers are particularly suitable for solutions with a high boiling point elevation and allows for flexible partial load operation, making it attractive for a wide range of applications.
Can the plant be used for both continuous and batch processes?
Yes, there are variants of the plant designed for both continuous and batch processes to meet a wide range of production requirements.
Other Processes








