
Partial Condensation

Functionality and Process of Partial Condensation
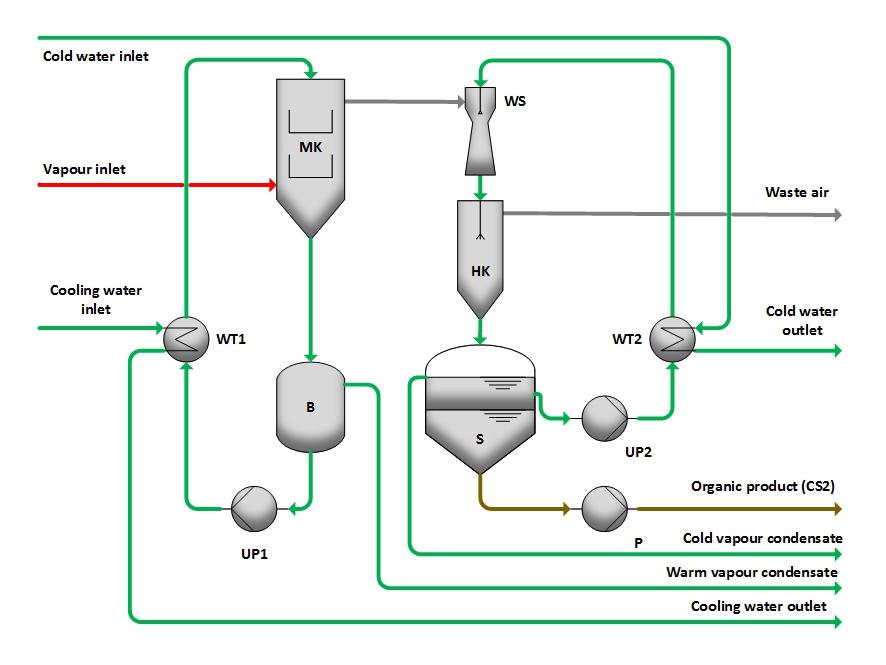
Partial condensation operates on the principle of selective gas condensation through temperature reduction. In viscose fiber production, exhaust streams containing steam, air, and CS₂ are first treated in a mixed condenser. Here, the majority of the steam condenses, while CS₂ remains gaseous.
The uncondensed substances are then further cooled in an auxiliary condenser, causing CS₂ and remaining steam to condense. In a settler, the condensed mixture separates into two phases for efficient extraction.
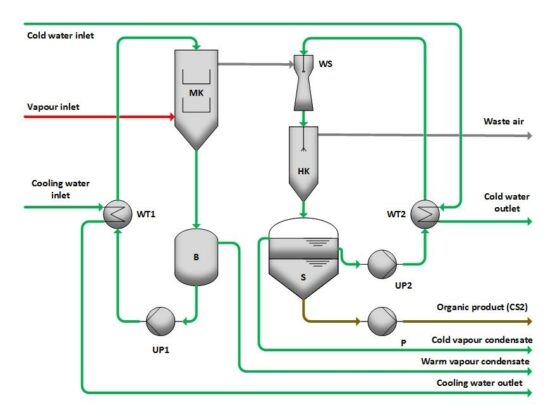
Partial Condensation Principle
Partial condensation is an efficient method for separating and recovering gaseous components from a carrier gas through targeted temperature reduction. This process is primarily used in the viscose fiber industry to recover valuable solvents while simultaneously reducing emissions.
Advantages of the Process
- Efficient recovery of solvents, particularly in explosive environments.
- Reduced energy requirements through a two-stage condensation process.
- Enhanced environmental compatibility by reducing emissions.
- Adaptability to various industrial applications.
Typical Applications and Examples
- Viscose fiber industry: Recovery of CS₂ from exhaust streams.
- Chemical industry: Separation and recovery of volatile organic compounds.
- Environmental technology: Treatment of industrial exhaust gases.
For more information about our partial condensation process and how it can optimize your production processes, please contact us. Contact us now!
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is partial condensation used in the viscose fiber industry?
It enables efficient recovery of CS₂, a vital solvent in viscose fiber production.
How does partial condensation contribute to environmental protection?
By recovering solvents and reducing emissions, it contributes to the reduction of environmental pollution.
Is the process suitable for explosive substances?
Yes, partial condensation is particularly designed for handling explosive substances.
How is energy efficiency achieved in partial condensation?
The two-stage condensation process significantly reduces the need for cooling energy.
Other Processes








