Evaporators

Evaporators play a central role in thermal separation processes. Typical applications are found in the concentration of solutions. Depending on the application, various types of evaporators are used.
Thanks to decades of experience in the field of evaporation and concentration technology, EBNER has comprehensive know-how in the design and manufacturing of evaporators of various types.
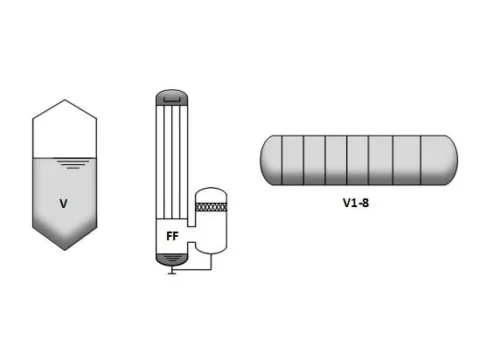
Types of Evaporators
- Vertical evaporators with forced circulation (FC): Use pumps to transport liquids, minimizing deposits in highly concentrated solutions.
- Vertical evaporators with natural circulation: Utilize density differences for circulation, suitable for less concentrated solutions.
- Falling film evaporators: Fast evaporation by flowing down in thin films, ideal for temperature-sensitive substances.
- Horizontal, multiple effect evaporators: Energy-efficient evaporation by using steam from previous stages.
Frequently Asked Questions
What distinguishes forced circulation from natural circulation evaporators?
Forced circulation evaporators use a pump for the circulation of the fluid, while natural circulation evaporators rely on density differences for circulation.
How energy-efficient are multiple effect evaporators?
Multiple effect evaporators reuse steam, leading to significantly lower energy consumption compared to single-stage systems.
Can evaporators be used for heat-sensitive materials?
Yes, evaporators such as falling film evaporators are particularly suitable for heat-sensitive materials as they allow a short residence time of the liquid on the heating surface.
How does the design of an evaporator affect product quality?
The design, such as the size and arrangement of the heating tubes, affects the evaporation rate and thus the concentration and purity of the final product.
Are evaporators maintenance-intensive?
This depends on the type of evaporator and the nature of the material to be evaporated. Ebner designs evaporators to be maintenance and cleaning efficient and user-friendly.