
Multiple Effect Evaporators

Function and Procedure of Multiple Effect Evaporation
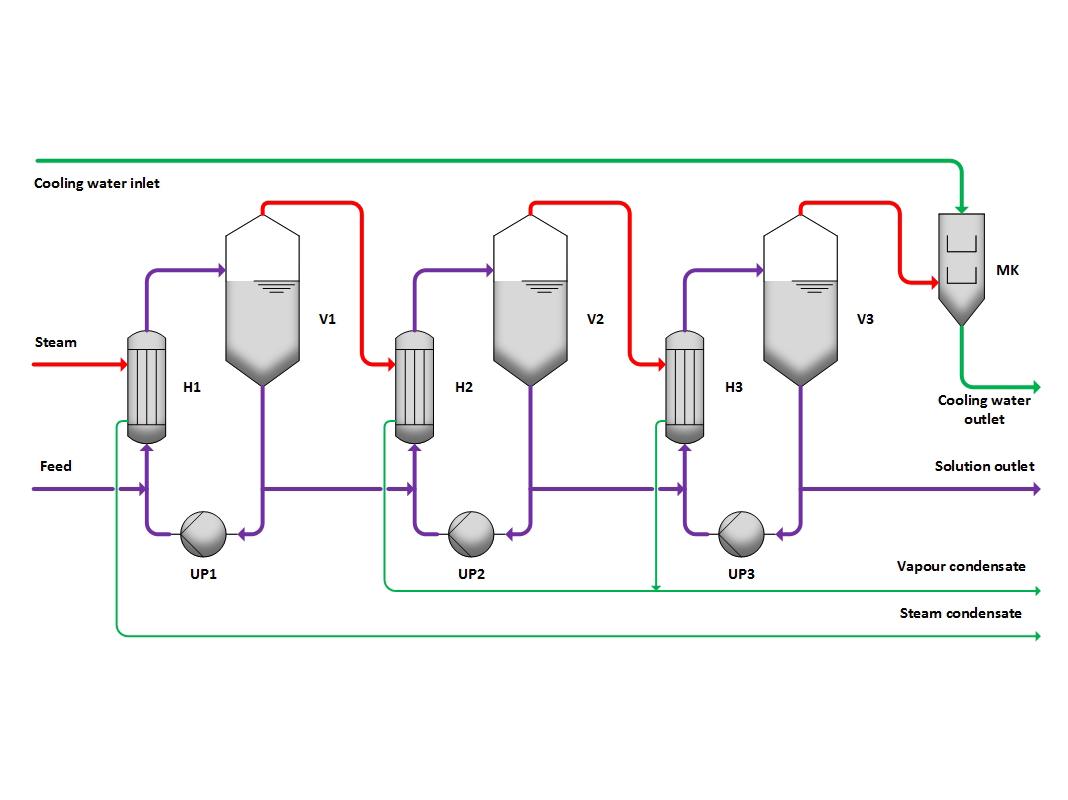
Multiple effect evaporation implements a system where the solution circulates through various evaporator stages (V1, V2, etc.). In the first stage, the solution is heated by a heater (H) with fresh steam and partially evaporated in the evaporator (V1).
The resulting vapor is used as a heating medium for the next stage, which operates at reduced pressure and thus lower temperature. This process is repeated through subsequent stages, each utilizing the vapors from the previous stage to save energy and increase efficiency. In the final stage, the vapor is typically condensed with cooling water. If necessary, the solution can be further evaporated to form salt crystals that can then be separated and dried.
Multiple Effect Evaporation Principle
Multiple effect evaporation optimizes energy requirements by efficiently using the vapors from previous stages to heat subsequent stages, achieving significant energy savings.
Advantages of Multiple Effect Evaporation
- Energy efficiency: Significant reduction in fresh steam usage by utilizing the vapors from the previous stage as a heating medium for the next stage.
- Flexibility: The system allows for flexible partial load operation and can be used for various applications and solvents.
- Scalability: Increasing the number of stages further reduces fresh steam consumption.
Variants and Customization Options
- Number of stages: Increasing the number of stages enables further reduction in fresh steam consumption and optimization of energy efficiency.
- Salt separation: The process can be implemented with or without salt separation, depending on the specific requirements of the process.
- Preheating concepts: Different preheating concepts can be integrated to adapt the process to specific conditions.
- Condensation: The vapor from the final stage can be condensed using mixing condensers or surface condensers.
- Solution entry point: The solution can be introduced either into the first stage (co-current) or the last stage (counter-current), resulting in either cold or hot discharge of the concentrate from the plant.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does multiple effect evaporation affect energy requirements?
By using the vapors from previous stages to heat subsequent stages, energy requirements are significantly reduced.
What advantages does multiple effect evaporation offer?
Multi-stage evaporation offers advantages such as reduced fresh steam consumption, increased energy efficiency, operational flexibility, and scalability by increasing the number of stages.
Can multiple effect evaporation be used for various solvents?
Yes, the process is suitable for a wide range of applications and solvents.
How is the concentrated solution discharged from the plant?
The concentrated solution can be discharged either cold (co-current) or hot (counter-current) from the plant, depending on which stage the solution is introduced.
How is salt separation achieved in multiple effect evaporation?
Further evaporation concentrates the solution enough for salt crystals to form, which can then, if desired, be separated and dried from the solution.
Other Processes








